Garage Radiant Floor Heat: Creating a Comfortable, Functional Space Year-Round
How Garage Radiant Floor Heat Turns Your Space Into a Comfortable, Functional Zone All Year

Garages have evolved far beyond vehicle storage. Today, they serve as workshops, fitness studios, hobby spaces, home offices, and climate-controlled car bays. But most garages share one thing in common: cold concrete floors that make the space uncomfortable during fall and winter.
Garage radiant floor heat has become the preferred heating method for homeowners and contractors who want consistent comfort, cleaner air, and energy-efficient performance. Instead of blowing warm air from a wall unit or ceiling heater, radiant systems heat the floor itself, allowing warmth to rise evenly and naturally through the entire space.
Whether you’re building new, upgrading a shop space, or converting a garage into living area, radiant floor heating transforms what was once an under-utilized space into an inviting, productive environment.
Why Radiant Heat Works So Well in Garages
Traditional heaters blast hot air into the room, creating uneven comfort and losing heat every time the garage door opens. Radiant systems, on the other hand, rely on thermal mass and conductive heat transfer. They warm the concrete slab itself, turning the garage floor into a steady, gentle heat source that holds warmth long after the system cycles off.
Advantages of a heated garage floor:
- Even, uniform heat from the floor up
- No drafts or dust circulation, ideal for workshops
- Protection for vehicles and tools by reducing condensation
- Energy-efficient performance, especially in cold climates
- Safe and silent operation with no exposed flames or heaters
- A more usable year-round space for work or recreation
In climates where winter temperatures are harsh, radiant heating is one of the best upgrades for comfort and property value.
Hydronic Radiant Systems: The Best Choice for Garages
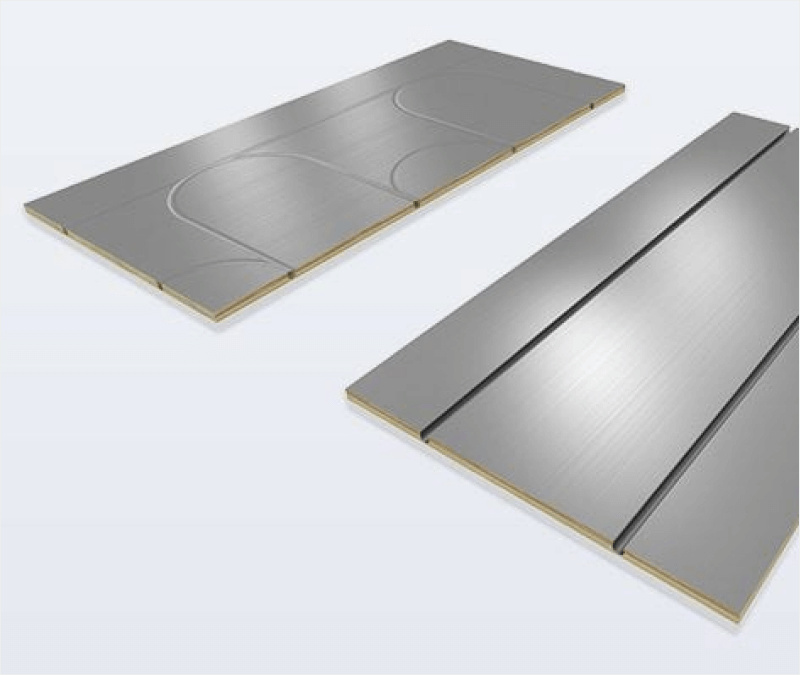
While small electric mats can work for tiny spaces or single work zones, most garages benefit from hydronic radiant heating, which uses warm water circulating through PEX tubing to heat the slab. Hydronic systems offer:
- Lower operating cost
- Better heat coverage
- Longer life span
- Compatibility with a wide range of heat sources, including efficient boilers and air-to-water heat pumps
For permanent garage comfort and long-term value, hydronic radiant is simply the most durable and scalable solution.
Installation Options: In-Slab vs. Above-Slab Radiant
Radiant floors in garages are typically installed in one of two ways.
In-Slab Radiant Heating (New Builds)
PEX tubing is attached to insulation or rebar before the concrete is poured. The slab encapsulates the tubing, creating long-term thermal mass. This is standard for new construction garages and offers outstanding durability.
Pros:
- Permanent, protected tubing
- Excellent heat retention
- No change in finished floor height
Considerations:
- Slow warm-up time since the slab must heat fully
- Repairs (rare) require slab access
Above-Slab Radiant Panels (Retrofit or Remodel)
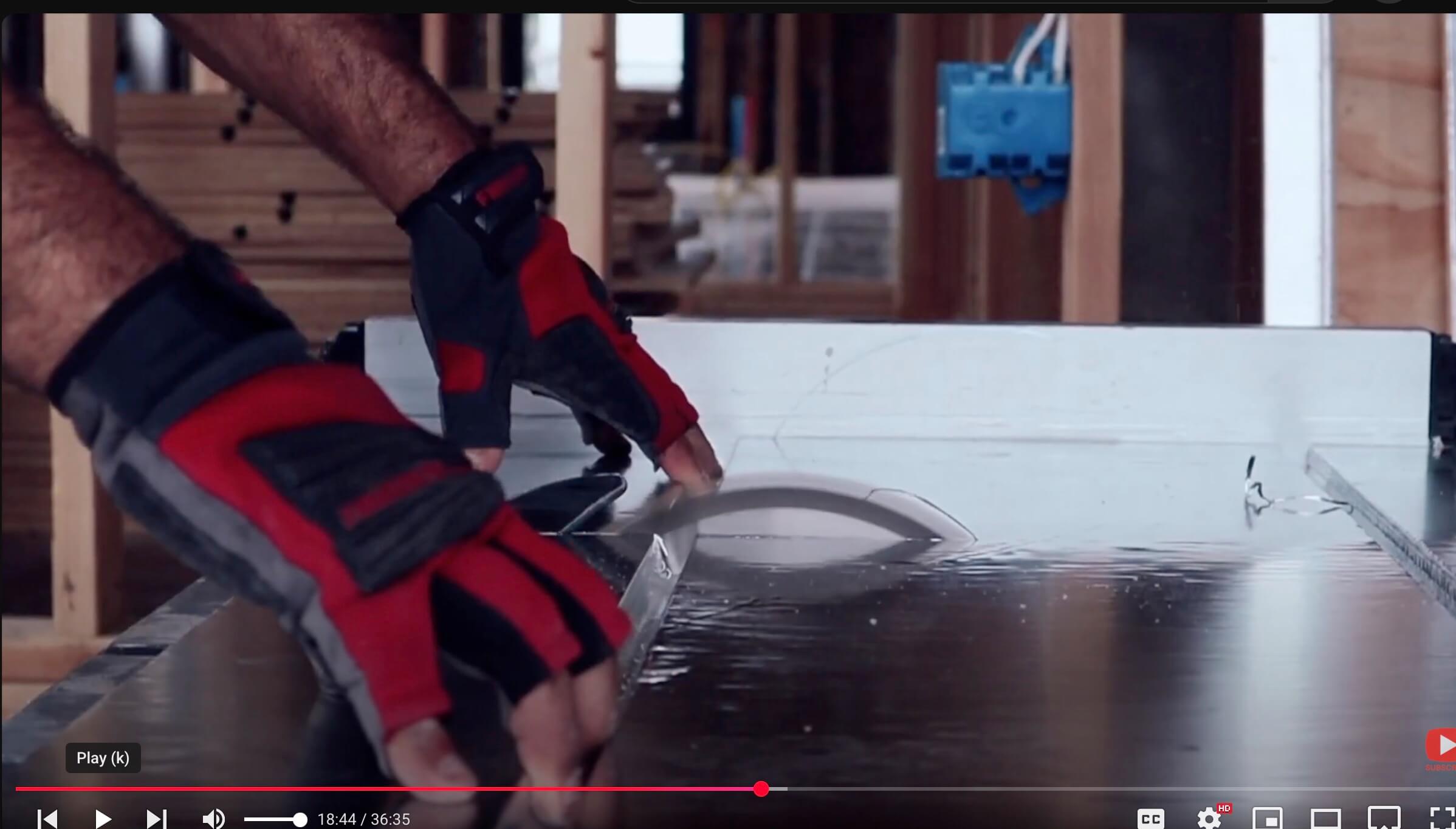
For existing garages, EPS-backed radiant panels allow hydronic heat to be installed over the concrete without breaking the slab. These engineered panels include aluminum heat-transfer layers and pre-cut PEX channels, meaning tubing installs quickly and efficiently.
Pros:
- Fast response time
- No concrete demo
- Cleaner installation, cuts like subfloor
- Ideal for workshops, finished garages, and conversions
Considerations:
- Adds some build-up height (low-profile options minimize this)
For many homeowners converting their garage into a gym, studio, or conditioned workspace, above-slab panels provide the best combination of performance, speed, and installation flexibility.
The Critical Role of EPS Insulation in Garages
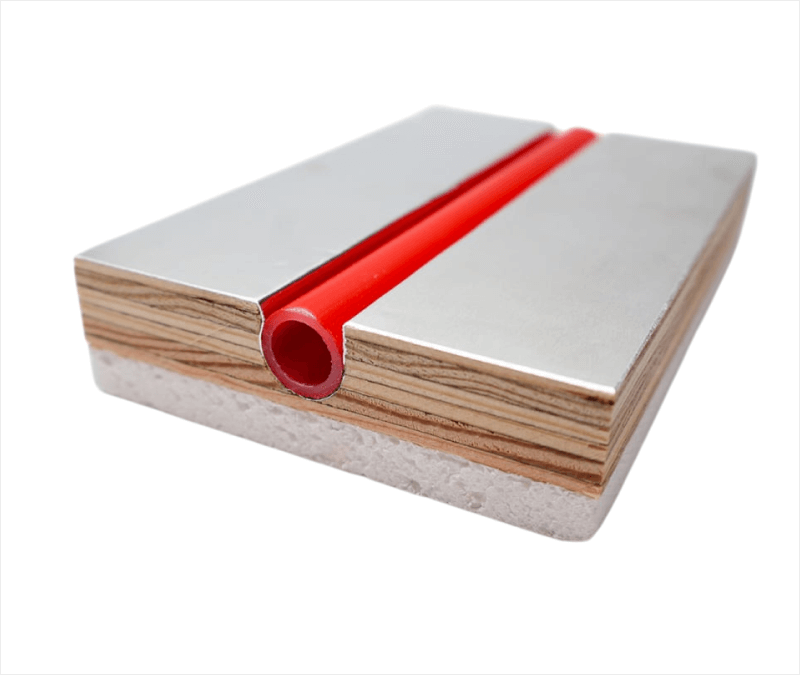

Concrete is a massive heat sink. Without insulation, much of the radiant energy travels downward into the ground instead of upward into the space. EPS insulation creates a thermal break and dramatically improves system efficiency.
Panels designed with an EPS layer help:
- Focus heat upward into the garage
- Reduce warm-up time
- Cut energy waste
- Improve comfort in cold-climate garages
In many modern radiant installs, especially above-concrete systems, EPS-backed aluminum radiant panels have become the preferred method due to performance and ease of installation.
Installation Timeline for Garage Radiant Heat
Understanding where radiant fits in the build schedule helps jobsite coordination run smoothly.
New Construction
- Sub-base prep and vapor barrier
- EPS insulation installed across the slab area
- PEX tubing placed and secured to insulation or rebar
- Concrete poured over the tubing
- Mechanical connection and commissioning
Existing Garage / Retrofit
- Clean, level existing slab
- Install radiant panels over concrete
- Snap tubing into panel channels per layout plan
- Pressure test and connect manifolds
- Install finished surface (epoxy, tile, LVP, engineered wood, etc.)
For remodels or shop setups, panels can be installed using typical carpentry tools, allowing general contractors or skilled homeowners to complete the panel and tubing portion before a plumber finishes the hydronic tie-in.
Flooring Options Over Heated Garage Slabs
Heated concrete floors can be finished in multiple ways:
- Polished or sealed concrete
- Epoxy coatings (popular for auto and workshop spaces)
- Tile for mudrooms and conditioned garages
- Engineered wood or LVP for garage conversions
The key is to follow manufacturer guidelines to ensure compatibility with radiant heat.
Real-World Use Cases
Radiant garage systems excel in:
- Home workshops and makerspaces
- Automotive storage and detailing garages
- Home gyms and wellness rooms
- Outdoor gear and mudroom connections
- Garage-to-living conversions
- Commercial service bays and industrial shops
Anywhere that floor comfort, air quality, and durability matter, radiant heat offers a long-term solution.
How Panel Systems Fit In Naturally
Modern radiant panel systems, including EPS-insulated options with aluminum heat-transfer surfaces, allow garages to be heated without concrete demolition or major renovation. These systems are engineered for efficient heat distribution, predictable tubing layout, and fast installation.
Many builders appreciate working with manufacturers who provide panel layouts and guidance, making installation smooth for carpenters, finish crews, and hydronic contractors alike.
With low-profile EPS designs available, garages gain warmth and efficiency without significantly raising floor height or complicating transitions into the home.
Final Thoughts
Radiant heat turns garages from cold, dusty storage spaces into high-performance living and working environments. Whether poured into a new slab or installed over an existing floor using insulated radiant panels, the system offers unmatched comfort, energy efficiency, and reliability.
From car enthusiasts to DIY woodworkers to homeowners expanding usable living space, heated garage floors are a smart, future-ready investment. With the right radiant components and proper installation sequence, the upgrade delivers long-term comfort from the ground up, literally.